Loops are very useful for running the same piece of code over and over again.
JavaScript supports different kinds of loops, the two main ones are:
- for - loops through a block of code a number of times.
- while - loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true.
For instance if we were programming a robot to walk forwards 6 steps, we could write the code like this:
stepForward()
stepForward()
stepForward()
stepForward()
stepForward()
stepForward()Or we could make the code simpler by using a for loop. This will repeat the stepForward() code 6 times.
for(let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
stepForward()
}for is correctFor is not correctFOR is not correct
The for loop takes three statements and then runs whatever code we specify. We put a ; (semicolon) after statement1 and after statement2. This let's the computer know when statement1 and statement2 end.
for(statement1; statement2; statement3)
{
// repeat this code
}- statement1 - this code runs once and sets up the variable we will use for our loop.
- statement2 - this is the condition for how many times the loop will run.
- statement3 - this changes the value of the variable in statement1.
Here is an example of a for loop what counts from 1 to 10. You will notice that we can use the variable x inside the for loop.
for(let x = 1; x <=10; x++)
{
basic.showNumber(x)
}So for the above example:
- statement1 -
let x = 1creates the variable x and sets it's value to 1. - statement2 -
x <= 10this is the condition that is checked every time. The loop will keep on repeating as long as x is less than or equal to 10. - statement3 -
x++this adds 1 to x each time the code is run.
Now let's try writing a for loop. Go to the https://makecode.microbit.org website, create a new project and switch to JavaScript. Try and write a for loop with the following statements:
- statement1 - create a variable called x and set it's value to 1.
- statement2 - specify the condition of x is less than 6.
- statement3 - add 1 to x each time.
- Put
basic.showNumber(x)as the code to run in the loop.
Run the code in the simulator and it should show the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. It should not show the number 6 as the condition is less than 6 (not less than or equal to 6).
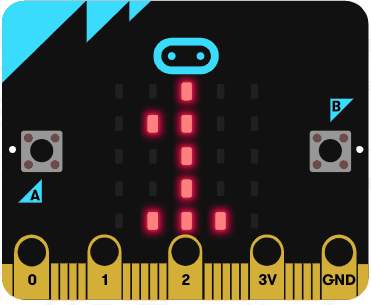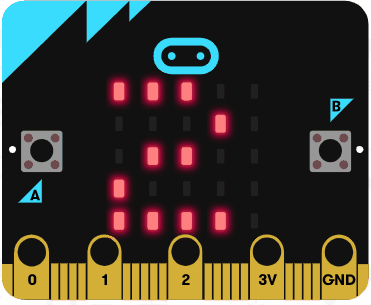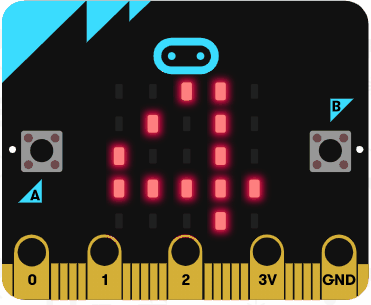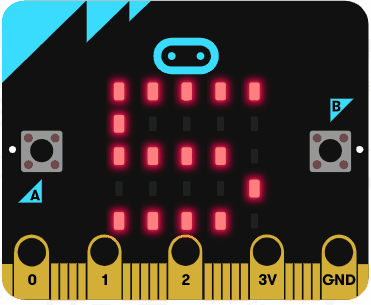
Now try and write some code to countdown from 10 to 0 using a for loop with the following statements:
- statement1 - create a variable called x and set it's value to 10.
- statement2 - specify the condition of x is greater than or equal than 0.
- statement3 - subtract 1 from x each time.
- Put
basic.showNumber(x)as the code to run in the loop.
The while loop takes one statement which is the condition (or conditions) under which the loop should keep on running.
while(condition)
{
// repeat this code
}- statement1 - this is the condition (or conditions) that the loop should keep on running until the condition is true.
Here is an example of a while loop what counts from 1 to 10.
let i = 1 // create the variable and set it to 1
while(i <= 10)
{
basic.showNumber(i) // show i
i++ // add 1 to i
}So for the above example:
- statement1 -
i <= 10this is the condition that is checked every time. The loop will keep on repeating as long as i is less than or equal to 10.
Notice that we put the code i++ inside the while loop to keep on adding 1 to i. What would happen if we did not keep on adding 1 to i?
This lesson is copyright of . Unauthorised use, copying or distribution is not allowed.
